Advanced Java - JDBC
Introduction to Java JDBC
JDBC stands for Java Database Connectivity. JDBC API is a Java API which is used to access tabular data, especially which are stored in the relational database. JDBC works with Java on platforms like Windows, MacOS, and UNIX.What is JDBC?
JDBC is used for connecting java programming language with databases. JDBC library has APIs for each task, which is mentioned below.- Creating a connection to a database.
- Creating statements for SQL or MySQL.
- Executing queries using SQL or MySQL in the database.
- Viewing & modifying the resulting records.
- Java Applications
- Java Applets
- Java Servlets
- Java ServerPages (JSPs)
- Enterprise JavaBeans (EJBs).
- Driver interface
- Connection interface
- Statement interface
- PreparedStatement interface
- CallableStatement interface
- ResultSet interface
- ResultSetMetaData interface
- DatabaseMetaData interface
- RowSet interface
- DriverManager class
- Blob class
- Clob class
- Types class
JDBC Architecture
JDBC Architecture consists of two layers:- JDBC API: It provides the application-to-JDBC Manager connection.
- JDBC Driver API: It supports the JDBC Manager-to-Driver Connection.
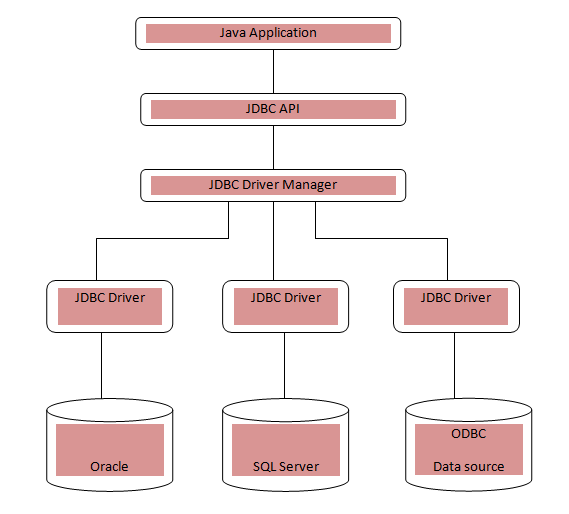
JDBC Driver
JDBC drivers implement the defined interfaces in the JDBC API, for interacting with your database server. Java.sql package contains classes and their behaviors and their main implementation is done in third-party drivers. The Third-party vendor implements the java.sql.Driver interface in their database driver. There are four types of drivers as following: Type 1: JDBC-ODBC Bridge Driver In Type 1 driver, a JDBC bridge accesses ODBC driver which is installed on each client machine. Data Source Name (DSN) is to be configured on the client machine which represents the target database. This type of driver is only for experimental use.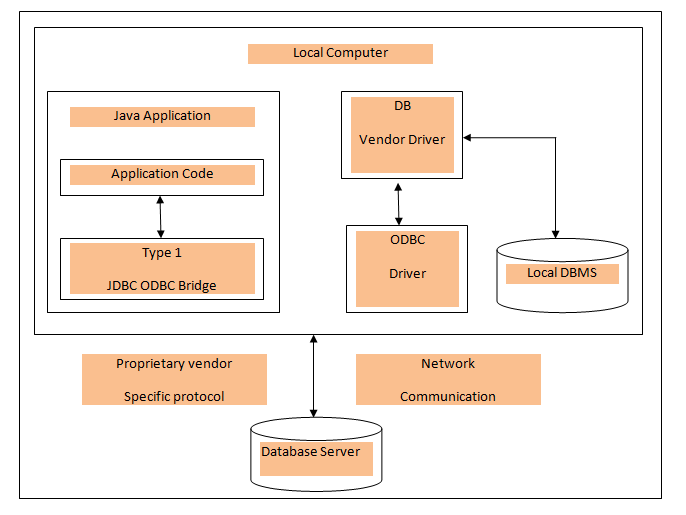 Type 2: JDBC-Native API
In Type 2 driver, JDBC API calls are converted into native C/C++ API
calls, these calls are unique to the database. These types of drivers
are provided by database vendors and it is used in the same manner as
the JDBC-ODBC Bridge. This driver which is provided by vendors must be
installed on each client machine. If the database is changed then the
native API also must be changed, because native API is specific to the
database.
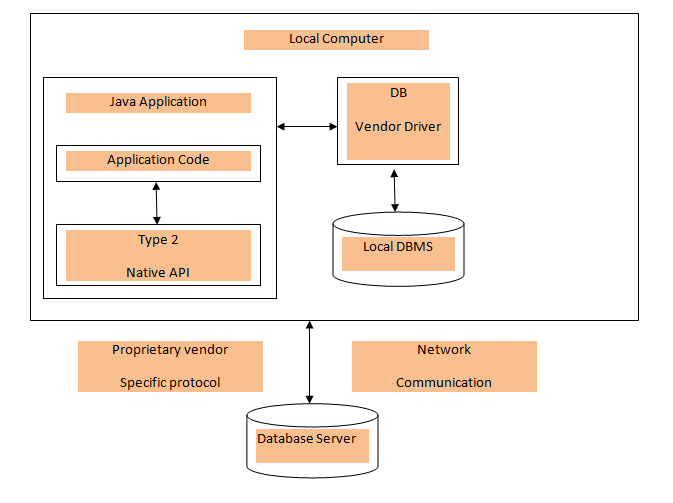
Type 2: JDBC-Native API
In Type 2 driver, JDBC API calls are converted into native C/C++ API
calls, these calls are unique to the database. These types of drivers
are provided by database vendors and it is used in the same manner as
the JDBC-ODBC Bridge. This driver which is provided by vendors must be
installed on each client machine. If the database is changed then the
native API also must be changed, because native API is specific to the
database.
 Type 3: JDBC-Net pure Java
In Type 3 driver, to access the database, a three-tier approach is used.
Standard network sockets are used by JDBC clients to communicate with
the middleware application server. These middleware application servers
translate socket information into call format which is required by the
DBMS and then forward it to the database server. As it does not requires
any code installation on the client that is why this kind of drivers
are extremely flexible.
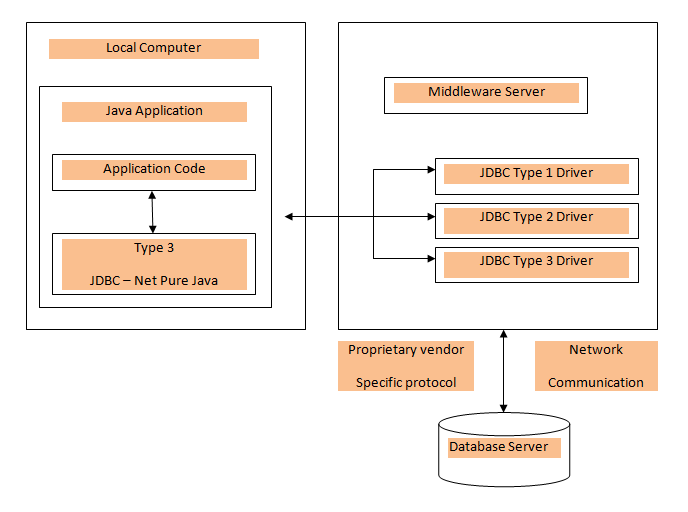
Type 3: JDBC-Net pure Java
In Type 3 driver, to access the database, a three-tier approach is used.
Standard network sockets are used by JDBC clients to communicate with
the middleware application server. These middleware application servers
translate socket information into call format which is required by the
DBMS and then forward it to the database server. As it does not requires
any code installation on the client that is why this kind of drivers
are extremely flexible.
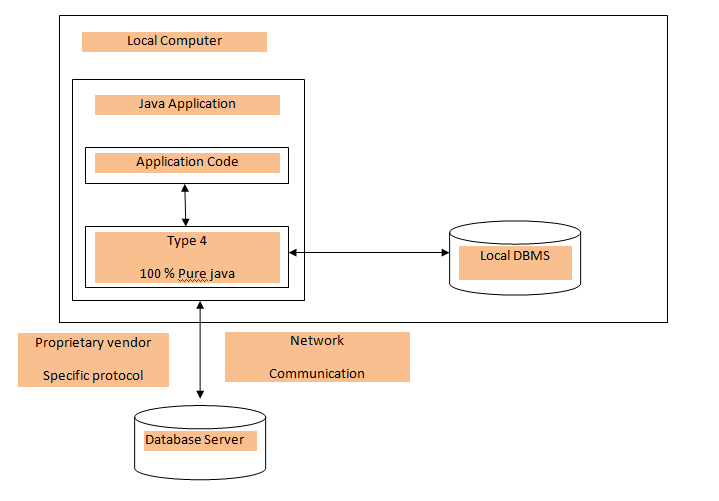
 Type 4: 100% Pure Java
In Type 4 driver, pure Java-based driver communicates with the vendor's
database directly through a socket connection. Type 4 driver has the
highest performance and it is provided by the vendor itself. It does not
require special software on the client or server that is why it is
extremely flexible and also these drivers can be downloaded dynamically.
Type 4: 100% Pure Java
In Type 4 driver, pure Java-based driver communicates with the vendor's
database directly through a socket connection. Type 4 driver has the
highest performance and it is provided by the vendor itself. It does not
require special software on the client or server that is why it is
extremely flexible and also these drivers can be downloaded dynamically.
Advantages of JDBC in Java
- If proper drivers are installed, any database can be read.
- Creates XML structure of data from the database automatically.
- No content conversion required.
- Query and Stored procedure supported.
- Can be used for both Synchronous and Asynchronous processing.
- Supports modules.
Disadvantages of JDBC in Java
- Correct drivers need to be deployed for each type of database.
- Cannot update or insert multiple tables with a sequence.
What is ResultSet?
- The
java.sql.ResultSetinterface represents the database result set, which is obtained after the execution of SQL query using Statement objects. - Object of ResultSet maintains a cursor pointing to the current row
of data in the result set. Initially, the cursor is located before the
first row. Then the cursor is moved to the next row by using the
next()method. Thenext()method can be used to iterate through the result set with the help of a while loop. If there are no further rows, thenext()method will return false. - Example for the creation of ResultSet is given below:
ResultSet rs = con.executeQuery(sqlQuery);
What is JDBC driver?
JDBC driver is a software component having various classes and interfaces, that enables the Java application to interact with a database.
To connect with individual databases, JDBC requires particular drivers for each specific database. These drivers are provided by the database vendor in addition to the database. For example:
- MySQL Connector/J is the official JDBC driver for MySQL and we can locate the
mysql-connector-java-<version>-bin.jarfile among the installed files. On windows, this file can be obtained at
C:\Program Files (x86)\MySQL\MySQL Connector J\mysql-connector-java-5.1.30-bin.jar.- JDBC driver of Oracle 10G is ojdbc14.jar and it can be obtained in the installation directory of an Oracle at
…/Oracle/app/oracle/product/10.2.0/server/jdbc/lib.
JDBC driver provides the connection to the database. Also, it implements the protocol for sending the query and result between client and database.
What is DriverManager in JDBC?
- JDBC DriverManager is a static class in Java, through which we manage the set of JDBC drivers that are available for an application to use.
- Multiple JDBC drivers can be used concurrently by an application, if necessary. By using a Uniform Resource Locator(URL), each application specifies a JDBC driver.
- When we load the JDBC Driver class into an application, it registers itself to the DriverManager by using
Class.forName()orDriverManager.registerDriver(). To check this, you can have a look into the source code of JDBC Driver classes. After this, when we callDriverManager.getConnection()method by passing the details regarding database configuration, DriverManager will make use of registered drivers to obtain the connection and return it to the caller program.
JDBC Net pure Java driver(Type 4 driver) is the fastest driver for localhost and remote connections because it directly interacts with the database by converting the JDBC calls into vendor-specific protocol calls.
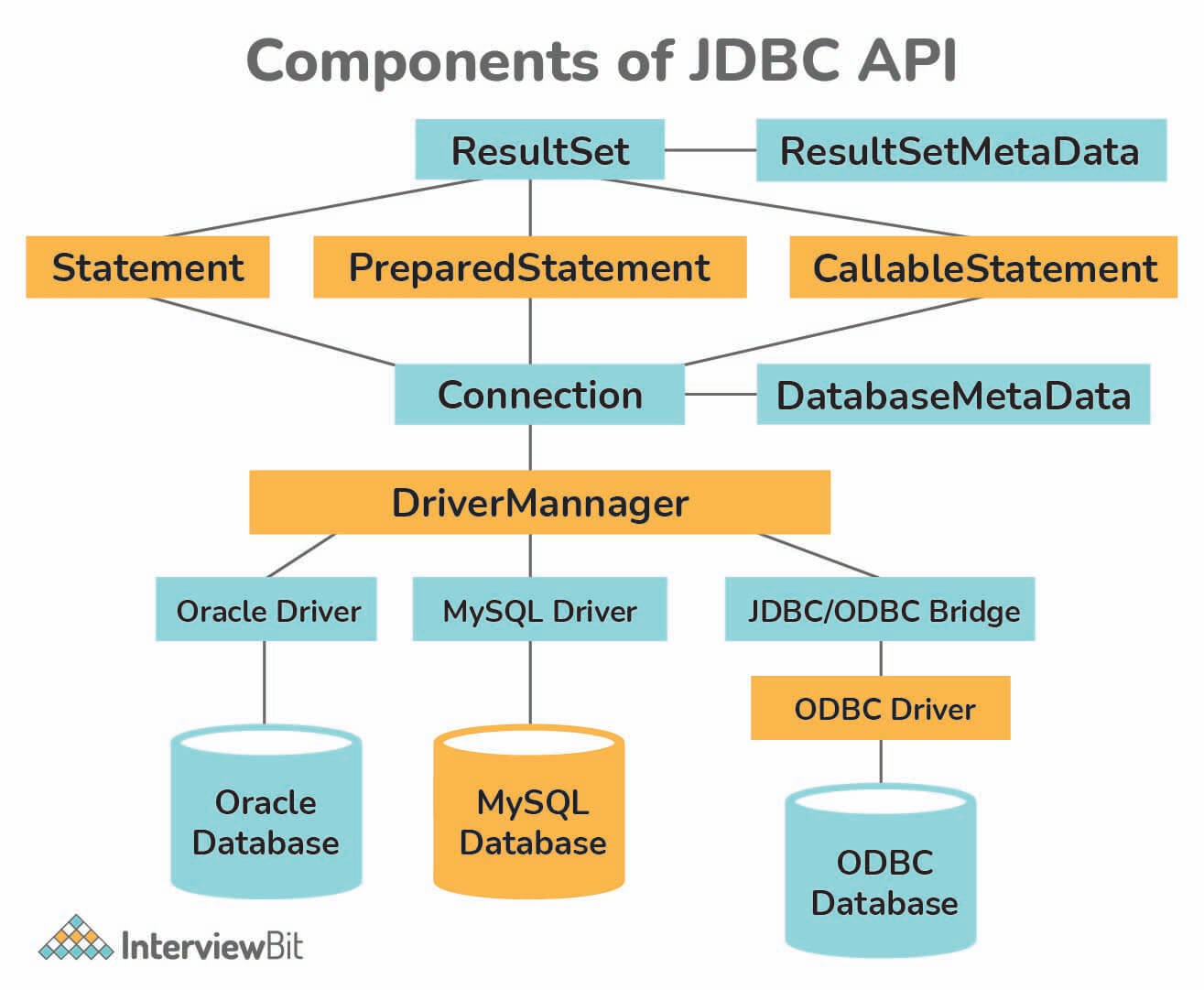
Q. Explain JDBC API components.
OR
Q.What is JDBC API and when do we use it?
Java DataBase Connectivity API allows us to work with relational databases. JDBC API interfaces and classes are part of java.sql and javax.sql
package. We can use JDBC API to get the database connection, run SQL
queries and stored procedures in the database server and process the
results. JDBC API is written in a way to allow loose coupling between
our Java program and actual JDBC drivers that make our life easier in
switching from one database to another database servers easily.
The java.sql package contains different interfaces and classes for JDBC API. They are:
Interfaces:
- Connection: The object of Connection is created by using getConnection() method of DriverManager class. DriverManager is the factory for connection.
- Statement: The object of the Statement is created by using createStatement() method of the Connection class. The Connection interface is the factory for Statement.
- PreparedStatement: The PreparedStatement object is created by using prepareStatement() method of Connection class. It is used for executing the parameterized query.
- ResultSet: The ResultSet object maintains a cursor pointing to a table row. At first, the cursor points before the first row. The executeQuery() method of the Statement interface returns the object of ResultSet.
- ResultSetMetaData: The ResultSetMetaData interface object contains the details about the data(table) such as number of columns, name of the column, column type etc. The getMetaData() method of ResultSet returns the ResultSetMetaData object.
- DatabaseMetaData: It is an interface that has methods to get metadata of a database, like name of the database product, version of database product, driver name, name of the total number of views, name of the total number of tables, etc. The getMetaData() method that belongs to Connection interface returns the DatabaseMetaData object.
- CallableStatement: CallableStatement interface is useful for calling the stored procedures and functions. We can have business logic on the database through the usage of stored procedures and functions, which will be helpful for the improvement in the performance as these are pre-compiled. The prepareCall() method that belongs to the Connection interface returns the object of CallableStatement.
Classes:
- DriverManager: It pretends to be an interface between the user and drivers. DriverManager keeps track of the available drivers and handles establishing a connection between a database and the relevant driver. It contains various methods to keep the interaction between the user and drivers.
- BLOB: BLOB stands for Binary Large Object. It represents a collection of binary data such as images, audio, and video files, etc., which is stored as a single entity in the DBMS(Database Management System).
- CLOB: CLOB stands for Character Large Object. This data type is used by multiple database management systems to store character files. It is the same as BLOB except for the difference, instead of binary data, CLOB represents character stream data such as character files, etc.
What is the difference between Statement and PreparedStatement?
| Statement | PreparedStatement |
|---|---|
| The query is compiled every time we run the program. | The query is compiled only once. |
| It is used in the situation where we need to run the SQL query without providing parameters at runtime. | It is used when we want to give input parameters to the query at runtime. |
| Performance is less compared to PreparedStatement. | Provides better performance than Statement, as it executes the pre-compiled SQL statements. |
| It is suitable for executing DDL statements such as CREATE, ALTER, DROP and TRUNCATE. | It is suitable for executing DML statements such as INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE. |
| It cannot be used for storing/retrieving images and files in the database. | It can be used for storing/retrieving images and files in the database. |
| It executes static SQL statements. | It executes pre-compiled SQL statements. |
| Less secured as it enforces SQL injection. | More secured as they use bind variables, which can prevent SQL injection. |
What is JDBC Connection? Explain steps to get JDBC database connection in a simple Java program.
Loading the driver: At first, you need to load or register the driver before using it in the program. Registration must be done once in your program. You can register a driver by using any one of the two methods mentioned below:
-
Class.forName(): Using this, we load the driver’s class file into memory during runtime. It’s not required to use a new or creation of an object.
The below given example uses Class.forName() to load the Oracle driver:
Class.forName(“oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver”);The MySQL Connector/J version 8.0 library comes with a JDBC driver class: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver. Before Java 6, we had to load the driver explicitly using the statement given below:
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");However, this statement is no longer needed, because of a new update in JDBC 4.0 that comes from Java 6. As long as you place the MySQL JDBC driver JAR file into the classpath of your program, the driver manager can find and load the driver.
-
DriverManager.registerDriver(): DriverManager is a built-in Java class with a static member register. Here we will be calling the constructor of the driver class during compile time.
The below given example uses DriverManager.registerDriver() to register the Oracle driver:
DriverManager.registerDriver(new oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver());For registering the MySQL driver, use the below-given code:
DriverManager.registerDriver(new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver(); ); Create the connections:
- After loading the driver into the program, establish connections using the code given below:
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);Here,
con: Reference to a Connection interface.
url: Uniform Resource Locator.
user: Username from which SQL command prompt is accessed.
password: Password from which SQL command prompt is accessed.
- Url in Oracle can be created as follows:
String url = "jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:xe";Where oracle represents the database used, thin is the driver used, @localhost is the IP(Internet Protocol) address where the database is stored, 1521 is the port number and xe represents the service provider.
All 3 parameters given above are of string type and are expected to be declared by the programmer before the function call. Use of this can be referred from the final code of an application.
- Url in MySQL can be created as follows:
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:33061/test1";Where localhost represents hostname or IP address of the MySQL server, 3306 port number of the server and by default, it is 3306, test1 is the name of the database on the server.
Create a statement:
- Once a connection establishment is done, you can interact with the database. The Statement, PreparedStatement, and CallableStatement JDBC interfaces will define the methods that permit you to send SQL commands and receive data from the database.
- We can use JDBC Statement as follows:
Statement st = con.createStatement();Here, con is a reference to the Connection interface used in the earlier step.
Execute the query:
- Here, query means an SQL query. We can have various types of queries. A few of them are as follows:
- Query for updating or inserting a table in a database.
- Query for data retrieval.
- The executeQuery() method that belongs to the Statement interface is used for executing queries related to values retrieval from the database. This method returns the ResultSet object which can be used to get all the table records.
- The executeUpdate(sql_query) method of the Statement interface is used for executing queries related to the update/insert operation.
Example:
int m = st.executeUpdate(sql);
if (m==1)
System.out.println("Data inserted successfully : "+sql);
else
System.out.println("Data insertion failed");Here SQL is the SQL query of string type.
Close the connection:
- So finally we have sent the data to the location specified and now we are at the end of our task completion.
- On connection closing, objects of Statement and ResultSet will be automatically closed. The close() method of the Connection interface is used for closing the connection.
Example:
con.close();
 Q. Implementation of JDBC MySQL database connection using Java program using statement interface.
Q. Implementation of JDBC MySQL database connection using Java program using statement interface.import java.sql.*;
public class JDBCTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:33061/BCA_STUDENTS";
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(URL, "root", "root");
String result = conn != null ? "DB Connected" : "connection Failed ";
System.out.println(result);
Statement st = conn.createStatement();
ResultSet rs = st.executeQuery("select * from student");
while(rs.next())
System.out.println(rs.getInt(1) + " "+ rs.getString(2) +" "+ rs.getString(3));
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.err.format("SQL State: %s\n%s", e.getSQLState(), e.getMessage());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} // ENDS MAIN
}
 Q. Implementation of JDBC MySQL database connection, CREATE, UPDATE,INSERT,SELECT(READ) DML operations using using PreparedStatement interface.
Q. Implementation of JDBC MySQL database connection, CREATE, UPDATE,INSERT,SELECT(READ) DML operations using using PreparedStatement interface.Q.Implementation of JDBC Oracle database connection using a Java program:
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.*;
class OracleCon
{
public static void main(String a[])
{
//Creating the connection
String url = "jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:xe";
String user = "system";
String password = "123";
//Entering the data
Scanner k = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter employee Id");
int empid = k.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter employee name");
String empname = k.next();
System.out.println("Enter employee address");
String address = k.next();
//Inserting data using SQL query
String sql = "insert into employee values("+empid+",'"+empname+"','"+address+"')";
Connection con=null;
try
{
DriverManager.registerDriver(new oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver());
//Reference to connection interface
con = DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
Statement st = con.createStatement();
int m = st.executeUpdate(sql);
if (m == 1)
System.out.println("Data inserted successfully : "+sql);
else
System.out.println("Data insertion failed");
con.close();
}
catch(Exception ex)
{
System.err.println(ex);
}
}
}

Comments
Post a Comment